
This will include an inspection of the head, chest, abdomen, pelvis, limbs, and spine. The emergency room doctor will conduct a thorough evaluation, beginning with a head-to-toe physical examination of the patient. The trauma team will perform a complete and thorough evaluation in the hospital emergency room. After the vital signs are stabilized, rescue workers will assess obvious bleeding and limb-deforming injuries.īefore moving the patient, the EMS team must immobilize the individual in a cervical (neck) collar and backboard. It may be difficult to assess the extent of their injuries on first evaluation.Īt the accident scene, EMS rescue workers will first check the patient's vital signs, including consciousness, ability to breathe, and heart rate. Patients with fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine that have been caused by trauma need emergency treatment. These injuries frequently cause serious spinal cord compression. This is an unstable injury involving bone and/or soft tissue in which a vertebra moves off an adjacent vertebra (displacement). It does not usually affect stability.įracture-dislocation. This uncommon fracture results from rotation or extreme sideways (lateral) bending. This type of fracture can occur in a head-on car collision when the upper body is thrown forward while the pelvis is stabilized by a lap seat belt.
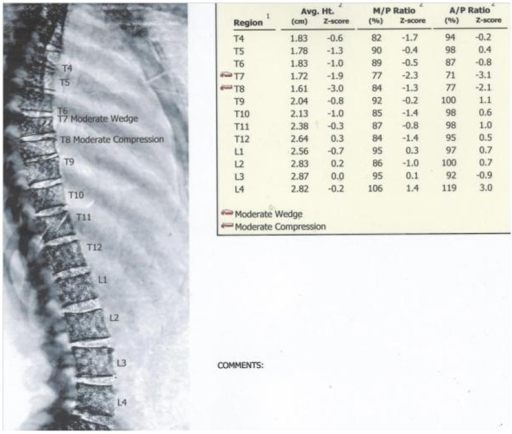
The vertebra is literally pulled apart (distraction). Extension Fracture Patternįlexion/distraction (Chance) fracture. Some fractures are stable, while others are significantly unstable (the bones have moved out of place). An axial burst fracture can sometimes result in nerve compression. It is often caused by landing on the feet after falling from a significant height. In this type of fracture, the vertebra loses height on both the front and back sides. 839-848.A compression fracture of the lumbar (lower) spine.Īxial burst fracture. Cement Leakage in Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: Identification of Risk Factors. The presence of other health care problems called comorbidities can slow down the healing process more than anything else. The real factors that seem to make the most difference are the patient's age, severity of fracture, type of fracture, and overall general health. Whether it is "better" or "worse" to have a fracture at one level over another is not something that has been researched. Likewise, a fall that results in the person hitting the back of the head and/or upper back could cause fractures higher up in the spine. Older adults who are bent forward with their spine curved in kyphosis (forward curve) have very different load and force placed on the vertebral bodies when compared with upright posture. For example, a fall on the buttocks is more likely to fracture the lumbar spine than the upper thoracic vertebrae. The mechanism of injury (e.g., fall, twist, cough) and force placed on the bone may determine where the fracture develops. So you can see that a fracture at T5 (upper end of the thoracic spine) is less common than most other locations. The numbers gradually declined from 15 fractures at 元 to 11 at L4 and five at L5. At the L1 to 元 levels, there were between 20 and 26 fractures. Then the largest number were at T12 (26 of the 177 fractures located here). The number increased slightly to around 14 between T8 and 11.

There were five fractures at T5, 10 fractures each at T6 and T7. But fractures occur anywhere from T5 to L5.Īccording to a recent study of 177 osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (in 89 adults), the distribution follows a bell-shaped curve. The most common vertebra affected is at the bottom of the thoracic spine where the lumbar spine begins (T12 and L1). Research shows that the distribution of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures varies. As a result, something as simple as coughing, twisting, or lifting can cause a vertebra to fracture. Spine bones that are weakened from osteoporosis may become unable to support normal stress and pressure. About 700,000 cases of compression fractures due to osteoporosis occur each year in the United States. A compression fracture of a spine bone (vertebra) causes the bone to collapse in height.Ĭompression fractures are most common in older adults as a result of osteoporosis (decreased bone density causing brittle bones). The surgeon mentioned this was "unusual." What is more typical? Does it matter what level is affected?Ī: From your reading you now know that compression fractures are the most common type of fracture affecting the spine. We are new to all this so we looked at your Patient Guide to Spinal Compression Fractures. Q: My 88-year-old mother just suffered her first vertebral compression fracture.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
